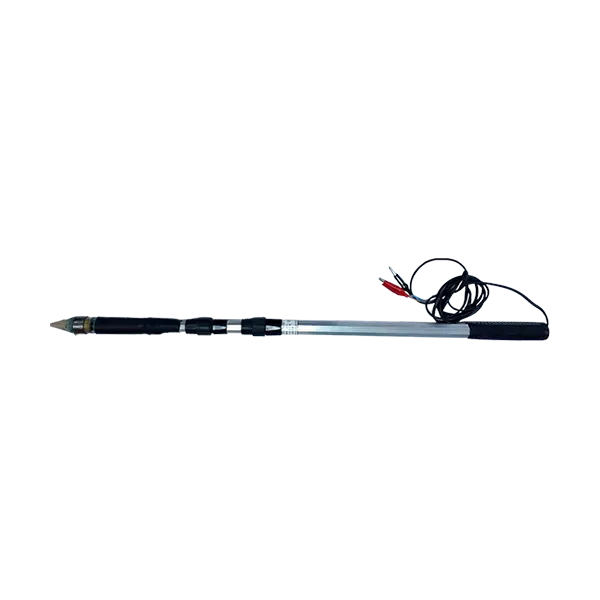
Copper sulfate portable telescopic reference electrode ESM-PT-800-1600 SHIK
The copper sulfate reference electrode is designed to provide galvanic contact with the ground when measuring the potential difference between metal underground structures and the ground (protective potentials on metal underground structures). The principle of the copper sulfate reference electrode is based on the redox reaction involving copper and its salts (copper sulfate). ESM-ОS SHIK is not subject to polarization, which means if a current is passed through the electrode, its potential will not change.
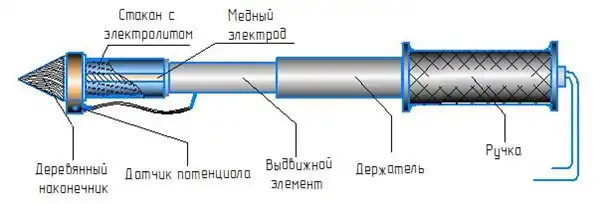
The classical scheme of a copper sulfate reference electrode is a copper rod inside a dielectric housing filled with a saturated solution of copper sulfate CuSO4, which is separated from the ground by a porous partition (ion exchange membrane). A solution of copper sulfate seeps through the ion-exchange membrane, moistens it and creates a galvanic contact between the copper rod and the ground through a solution of copper sulfate. The resulting constant potential difference at the "copper – saturated copper sulfate solution" boundary is compared with the potential difference at the "protected object — surrounding soil" boundary using instruments.
For convenience, the glass is fixed on a holder (duralumin tube), with a handle. The measuring wire from the copper electrode is connected to the terminal located under the handle.
The electrode in the pushed state has a length of 0.8 m, in the extended state – 1.6 m and is adjustable according to the situation.