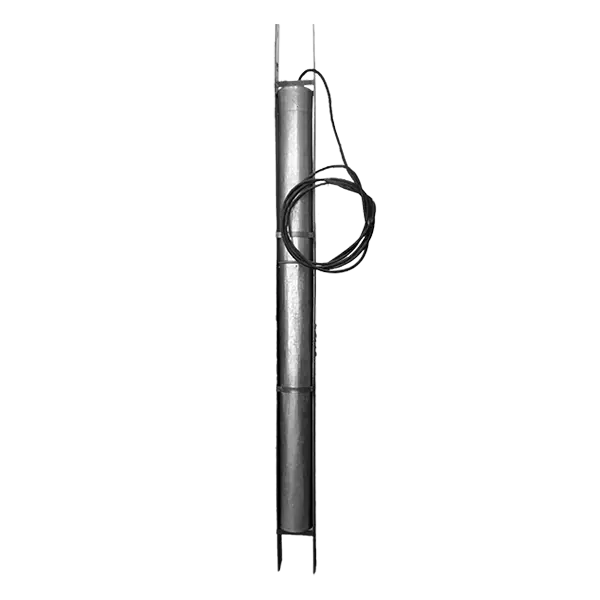
Anode grounding iron-silicon AZZHK-GU SHIK (deep, packed)
Anode earthing device ferro-siliceous AZZHK-GU SHIK – earthing devices designed to work in cathodic protection circuits of main gas and oil pipelines, underground and surface reservoirs of petroleum products, gas and water, underground cables, structures on piles, casing columns, wells, working grounding of power lines and other metal structures in contact with soil and water, regardless of the specific gravity resistance of the medium.
Earthing devices are designed to work complete with cathodic protection converters in any soil and climatic conditions when the electrodes are located below the depth of soil freezing.
The earthing device is a ferrosilide electrode placed in a galvanized tube with a metal guide structure filled with graphite filling, equipped with a cable outlet for connection to the main supply cable from the converter of the cathodic protection station.
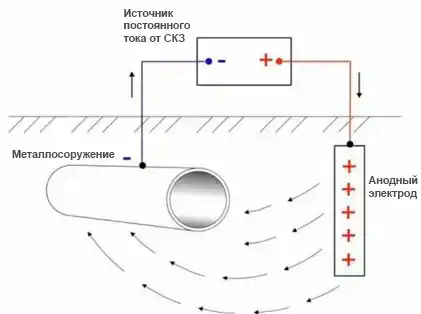
The principle of operation of the anode earthing device is aimed at compensating the negative charge of the soil with positive ions.
The reason for the corrosion of metal in the ground is a high level of moisture, heterogeneous structure and high acidity. As a result, different potentials appear on the surface of the metal product, provoking the appearance of rust.
An additional negative factor that accelerates the destruction of metal is stray currents that appear due to movement on the surface of electric vehicles, power stations, towers of mobile operators and other equipment.
The installation of an anode earthing device guarantees compensation of the negative charge and thereby prolongs the service life of metal products. One grounding is able to protect any metal located underground — pipes, containers, flat surfaces, etc.